Physiologically Attentive
User Interfaces
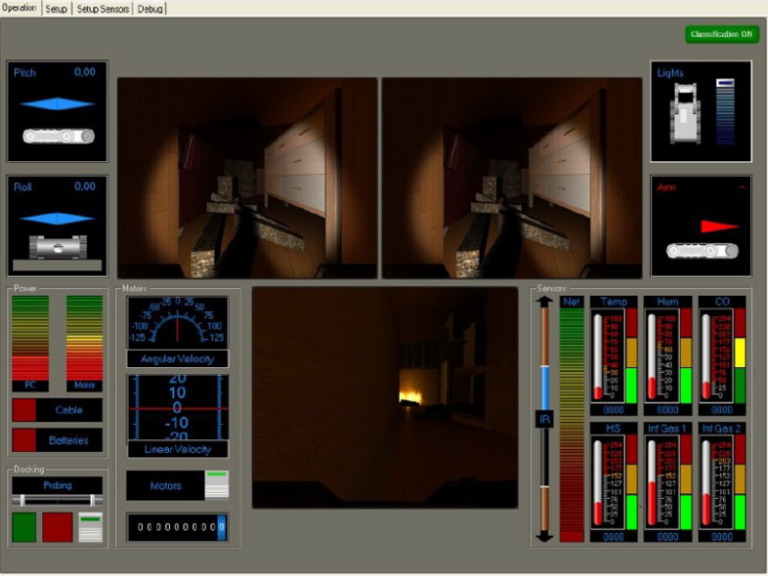
The GUI adjusts the displayed information when the operator is under high workload.
A novel system that aims to:
- Reduce Workload and Stress
- Increase the operator’s Effectiveness
Classification of the Emotional State of the Operator:
- Rest State: Original GUI
- Stress State: increased maximum speed
- High Cognitive Workload State: simplified GUI
Physiologically Attentive User Interface for Improved Robot Teleoperation

Description:
Interfaces developed for robot teleoperation can be particularly complex, often displaying large amounts of information, which can increase the cognitive overload that prejudices the performance of the operator.
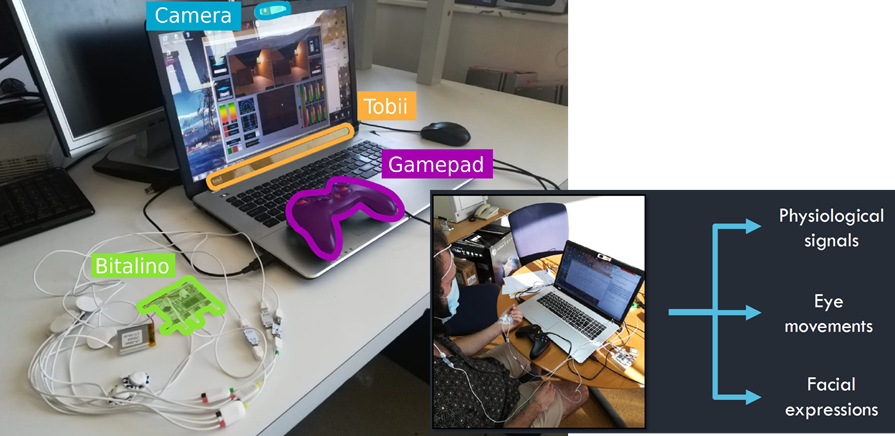
This project addresses this challenge by developing a Physiologically Attentive User Interface (PAUI) prototype. The proposed PAUI analyses physiological data, facial expressions, and eye movements to classify three mental states (rest, workload, and stress).
An Attentive User Interface (AUI) is then assembled by recycling a pre-existing GUI, which is dynamically modified according to the predicted mental state to improve the user’s focus during mentally demanding situations.
Acknowledgments:
This project was supported by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT, Portugal), through projects UIDB/50009/2020, UIDB/04466/2020 and UIDP/04466/2020.
Read more:
- Tavares, A., Silva, J. L., & Ventura, R. (2023). Physiologically Attentive User Interface for Improved Robot Teleoperation. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (pp. 776-789). ACM.
- Singh, G., Bermúdez i Badia, S., Ventura, R., & Silva, J. L. (2018). Physiologically attentive user interface for robot teleoperation: real time emotional state estimation and interface modification using physiology, facial expressions and eye movements. In 11th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (pp. 294-302). SCITEPRESS-Science and Technology Publications.